What is DNS?
Domain Name System, or DNS for short, enables you to create a custom domain name, which is easier for your visitors to remember.
The Fully Qualified Domain Name, or FQDN for short, is the complete address consisting of a domain name and a hostname.
Note: You can learn What Different DNS Records Mean using our guide.
What is a DNS resolver?
An open DNS resolver is a public name server that resolves recursive DNS lookups. In simple terms, a DNS resolver takes the website names we recognize and translates them to IP addresses. DNS servers use ports 53/TCP and 53/UDP.
Unfortunately, open DNS resolvers are vulnerable to DNS amplification and DNS spoofing attacks.
DNS Amplification attack
A DNS Amplification attack is a type of Denial of Service (DoS) attack that utilizes open DNS resolvers to flood servers/networks with unwanted traffic, which is meant to overwhelm or even take down the targeted infrastructure.
It is possible to protect systems against DNS amplification attacks. The simplest thing you can do is limit the IP addresses that the server performs recursive DNS lookups for.
DNS Spoofing attack
DNS Spoofing, also known as cache poisoning, is another type of DNS attack. During this attack, wrong information is introduced to the DNS cache. This is done to redirect visitors to the wrong websites.
What is a Portmapper?
A portmapper, also known as RPCbind, is an ONC RPC (Open Network Computing Remote Procedure Call) service. It is responsible for mapping RPC service numbers to network port numbers. Because of this service, when RPC clients call, the portmapper informs whether to use port 111/TCP or port 111/UDP.
Similarly to DNS resolvers, portmappers have been used in DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks. Due to this, some may consider disabling RPCbind services.
How to disable recursion
If you restrict recursion, you may be able to prevent DNS Amplification and DNS Spoofing attacks. Follow the steps below to learn how to disable recursion on different systems.
Windows
- Open DNS Manager.
- Right-click the chosen DNS server and click Properties.
- Move to the Advanced tab.
- Go to Server options and mark Disable Recursion.
- Click OK.
BIND 9.X DNS Servers
- Locate the named.conf file (located in /etc/bind/named.conf or /etc/named.conf).
- Open the file using the preferred editor.
- Go to the Options section, enter the data below and then restart.
allow-transfer {"none";};
allow-recursion {"none";};
recursion no;
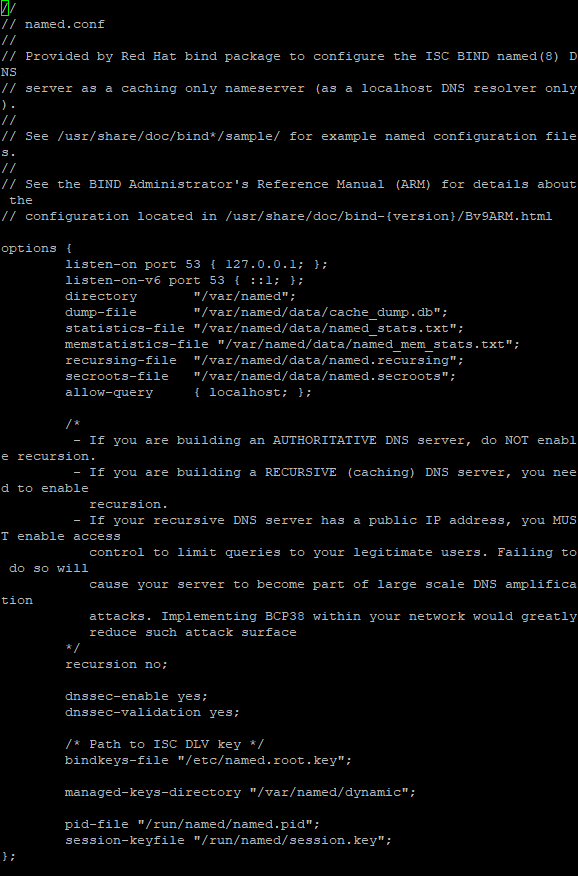
CentOS
- Log in to the server using root credentials.
- Find the file named named.conf.
- Replace recursion yes with recursion no.
How to disable portmapper on Linux/Ubuntu/Debian
Open the Terminal and use the following command to remove RPCbind:
# apt-get remove rpcbindIn conclusion
You are free to leave your 53 and 111 ports open, but because that may cause vulnerabilities, some users choose to disable these ports.
